If you’re shopping for a diamond, carat weight is probably one of the important things you’re considering. It seems like a straightforward measurement, but there is more to it than a simple number. Here’s essential information you need to know.
In this post, we cover:
What Is Carat Weight?
Diamond weight is stated in metric measurements called carats. One carat is equal to 200 milligrams, which is 1/5 of a gram or 0.20 gram. There are 142 carats in an ounce. Carat is also the standard unit of weight for most gemstones.
The modern carat system has its roots in the carob seed, which comes from the locust tree. Because the small seeds are fairly uniform in size and weight, they were a useful standard for determining the weight of a gem. Early gem merchants and jewelers used carob seeds as counterweights in hand-held balance scales.
Carat weight was standardized as 0.20 gram in the early twentieth century. This gave trade professionals a uniform and universally accepted weight standard for diamonds.

Notice that the seeds from the carob pods are nearly identical in size. Photo: Orasa Weldon/GIA
Carat is abbreviated as “ct” and weights are typically given to two decimal places: 1.00 ct, 0.76 ct, 1.57 ct.
Like the dollar, a carat is made up of 100 parts, called “points” and abbreviated as “pt.” An easy way to remember this is to think of carats as dollars and points as pennies. They’re even written the same way: $1.34 means one dollar and 34 cents, and 1.34 ct means one carat and 34 points.”
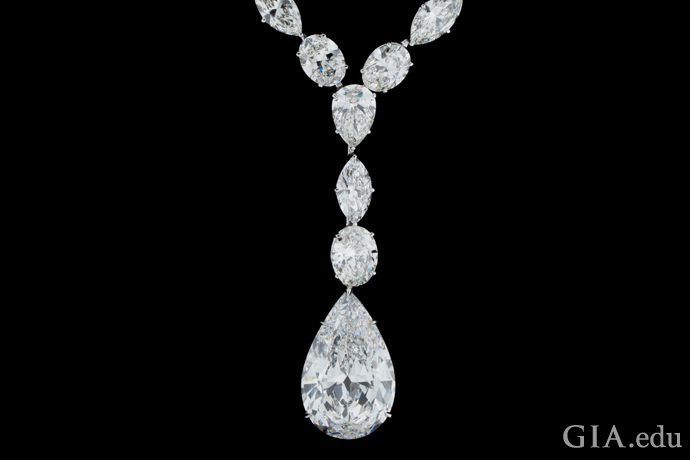

If you like big diamonds, you’ll love this necklace. The large pear shape weighs 25.04 ct, and it is suspended from another 64.24 carats of glittering diamonds. Photo: Robert Weldon/GIA. Courtesy: Chatila
How Does GIA Measure Diamond Carat Weight?
When a diamond is submitted to GIA, one of the first steps in the grading process is to determine its weight. To ensure precision, accuracy and consistency, GIA uses an electronic micro-balance scale to weigh each diamond. GIA adheres to strict calibration and maintenance procedures for its devices. These procedures exceed the manufacturer’s recommendations. In addition, the laboratory monitors and controls environmental conditions that might affect the quality of the results, such as room temperature and humidity.

Diamonds submitted to GIA are weighed on an extremely sensitive electronic micro-balance scale. Photo: Valerie Power/GIA
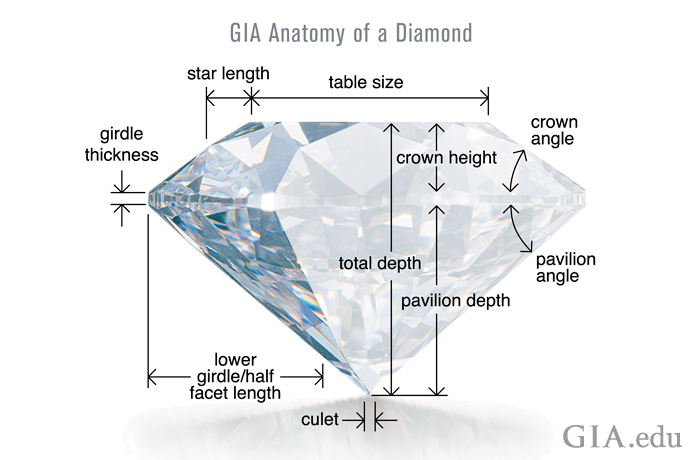
The diamond’s dimensions are also measured. An optical measuring device captures the diamond’s measurements (length and width), as well as its proportions and facet angles, which will eventually inform the diamond’s cut grade.
Diamond Carat Weight and Rounding Up (or Down)
While most trade professionals typically weigh diamonds to a thousandth of a carat (three decimal places), GIA weighs diamonds to the fifth decimal place – a hundred thousandths of a carat, to ensure maximum precision and provide an identifying characteristic.
The rounding rules GIA follows are also stricter than normal mathematical rounding rules. As mentioned above, a diamond’s carat weight is conventionally stated to two decimal places (0.71 ct, 1.34 ct). To arrive at this number, GIA rounds up to the next higher hundredth only if there’s a nine in the thousandth place. For example, a diamond that weighs 1.769 ct would be rounded up to 1.77 ct, but one that weighs 1.768 ct would be rounded down to 1.76 ct. Such differences in carat weight might seem small, but they can make a significant difference in price.

Get a sense of relative diamond size with this photo. From left to right: a yellow princess cut (0.86 ct), a pink round brilliant cut (0.68 ct), a gray-blue round brilliant (0.56 ct), a gray round brilliant (0.30 ct) and a blue-green round brilliant (0.15 ct). Photo: Robert Weldon/GIA
Once the diamond has been graded, its carat weight and dimensions — as well at its color, clarity and cut grade (if applicable) — are clearly documented on a GIA diamond grading report. Also included is full disclosure of any diamond treatments detected during the process.

The diamond’s weight is prominently stated on a GIA Diamond Grading Report. Photo: GIA
Why Is Carat Weight Important?
All other factors being equal, the price of a diamond increases as its carat weight increases. Since diamonds 1.00 ct or larger are comparatively rare, prices jump dramatically for these gems.
Carat weight also helps you compare prices between diamonds with different weights but the same color, clarity and cut grades, allowing you to compare the per carat price for each stone to see where you’re getting the best value.
Carat Weight and Shopping Considerations
Here are a few concepts related to carat weight that you should be aware of as you’re shopping:
Carat Weight and Gemstone Size – Two Different Things
It’s a common mistake to equate a gem’s carat weight with its physical dimensions. After all, it seems logical that a larger stone will weigh more. This is true if you’re comparing two stones of the same gem material – like a diamond to a diamond, or an aquamarine to an aquamarine.
However, size is a function of the gem material’s specific gravity – the ratio of the weight of a gem to that of an equal volume of water. Materials with different specific gravities (densities) will have different sizes for the same weight (think of an ounce of lead compared to an ounce of feathers). For example, the specific gravity of diamond (3.52; that is, 3.52 times the same volume of water) is lower than that of ruby (4.0), so a one-carat diamond will be larger than a one-carat ruby.
The bigger the diamond, the more bang for your buck?
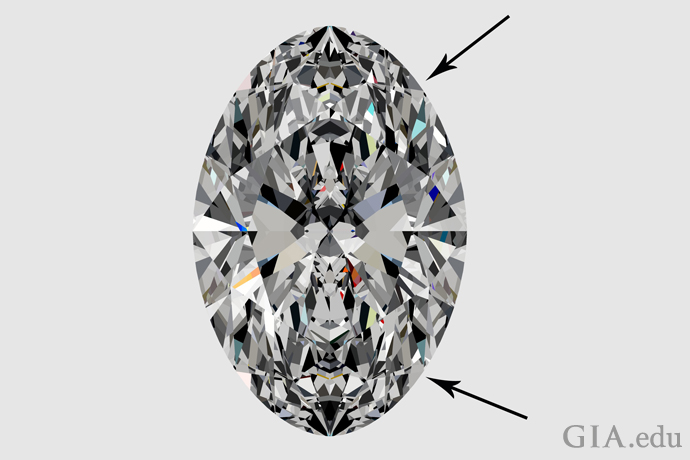
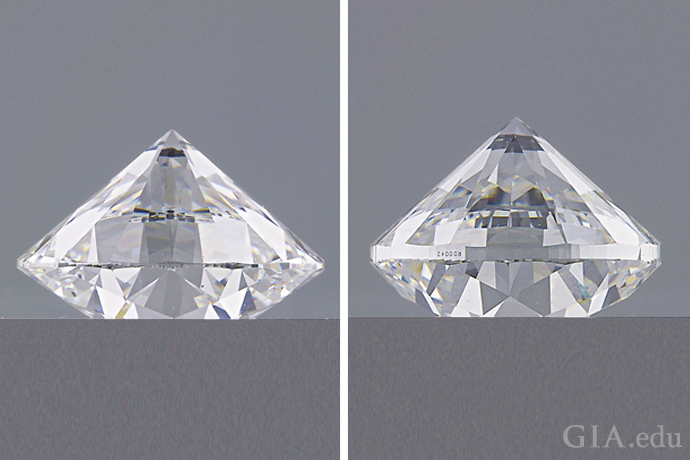
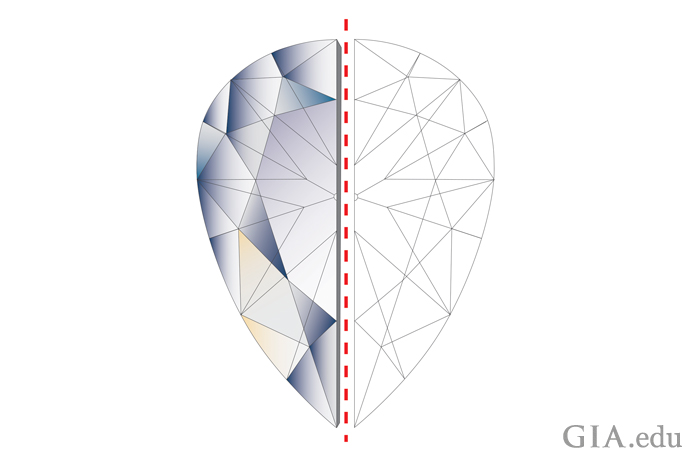
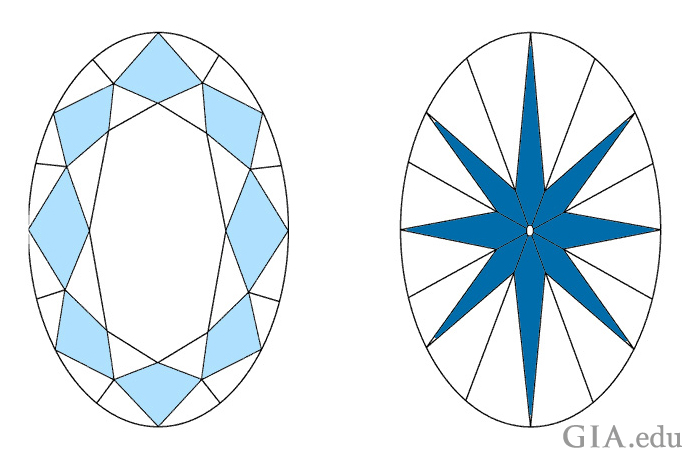
Not always. When it comes to diamonds, greater carat weight does not guarantee that the diamond will look bigger. For example, a poorly cut diamond may be too deep and have weight hidden below the girdle. You won’t see this weight when the diamond is mounted, and it won’t make the diamond more appealing – but the diamond will weigh more.

Excessive bulge, shown by the gray areas on either side of the outline, adds to a diamond’s weight without contributing to its beauty or perceived size when viewed face-up. Illustration: Peter Johnston/GIA
Magic Sizes
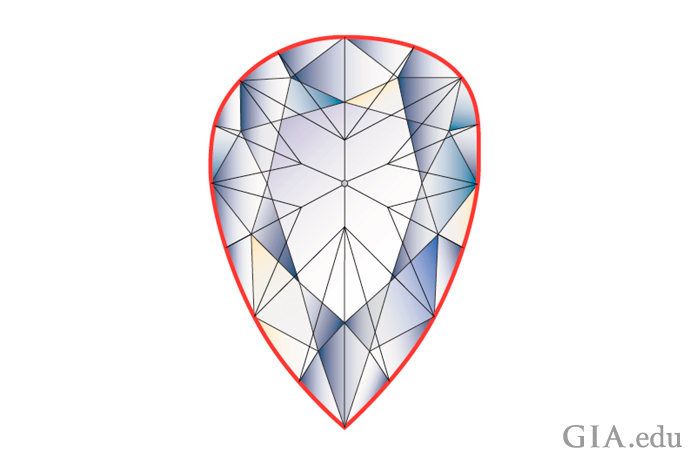
As mentioned earlier, for diamonds that are equal in every way, diamond value increases as weight increases. At certain weight boundaries, called “magic sizes,” the price per carat increases significantly. That’s because these boundaries or thresholds coincide with popular weights, and popularity means greater demand and therefore higher prices for these weights. This is especially true at the magic one-carat size.
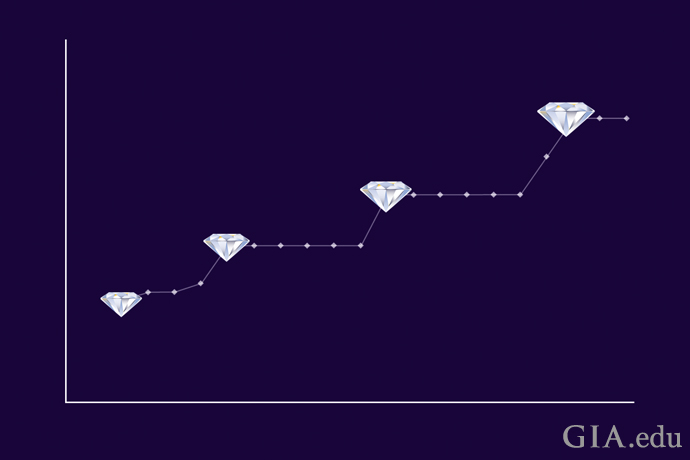
Diamonds increase in price at magic sizes like 0.25 ct, 0.50 ct, 0.75 ct and 1.00 ct. Illustration: Peter Johnston/GIA
A quick comparison of two diamonds shows how magic sizes can affect price. If one diamond weighs 0.96 ct and another weighs 1.02 ct, the 6 pt (0.06 ct) difference in size is almost imperceptible. But if both are D-color round brilliants with identical clarity and cut, the difference in cost is significant. The fact that the second diamond is slightly over the “magic” one-carat threshold may cause its price to be as much as 20 percent more.
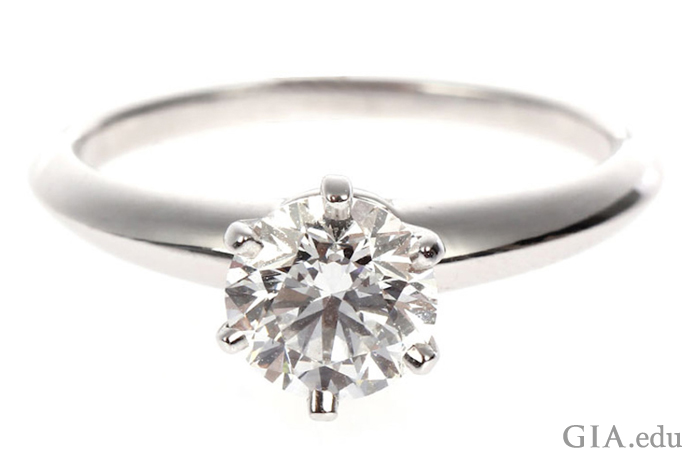

The 1.07 ct diamond in this Tiffany & Co. ring is a magic size. Courtesy: TrueFacet
Nevertheless, for some people carat weight is symbolic, so they will pay the higher price to reach the magic size.
There is another side to magic sizes – if you think they’re unimportant, you can look for a diamond that weighs slightly less than one of these boundaries and save money.
Carat weight isn’t everything
If you want the largest diamond you can afford, you’ll have to sacrifice clarity, color and/or cut, which may mean sacrificing beauty and sparkle. Choosing a diamond means prioritizing the 4Cs, and then making some compromises. Here is a thoughtful look at determining what’s the most important C for you.
Total Carat Weight
Understanding diamond terminology is essential if you’re going to make a smart purchase decision. “Total carat weight” (abbreviated tcw) is the combined weight of all the diamonds in a piece of jewelry that only contains diamonds.
An engagement ring set with many small melee diamonds weighing 2.15 tcw will cost significantly less than a solitaire engagement ring set with a single 2.15 ct diamond. Again, think size/rarity/price.

This Tiffany & Co. engagement ring has a cushion cut diamond, weighing 0.84 ct, surrounded by 0.06 carats of natural pink diamonds and 0.34 carats of melee. The total carat weight is 1.24 tcw. Courtesy: TrueFacet.
If an engagement ring has gems other than diamonds in it, the combined weight of all the stones is called “total gem weight.”
The Difference between Carats, Karats and Carrots
Here’s a last bit of terminology that we need to explain. As you know by now, a carat is a metric unit of measure to describe the weight of a diamond and other gemstones. Karat (abbreviated as K) is the measure of the purity of gold. A karat has 24 parts, so 18K gold would mean that the metal is 18 parts gold and 6 parts of other metals (such as copper, silver and/or zinc). Carrots, well, that’s something rabbits are famous for eating.
A diamond engagement ring is a once-in-a-lifetime purchase that is a symbol of your love. Understanding carats and points can help you with this “weighty” decision.
In addition to carat weight, a GIA grading report contains a wealth of information about your diamond. If you’d like to dig deeper, you’ll be interested in the other articles in this series:
GIA Diamond Grading Reports: Understanding the Diamond Color Grade
GIA Diamond Grading Reports: Understanding the Diamond Clarity Plotting Diagram
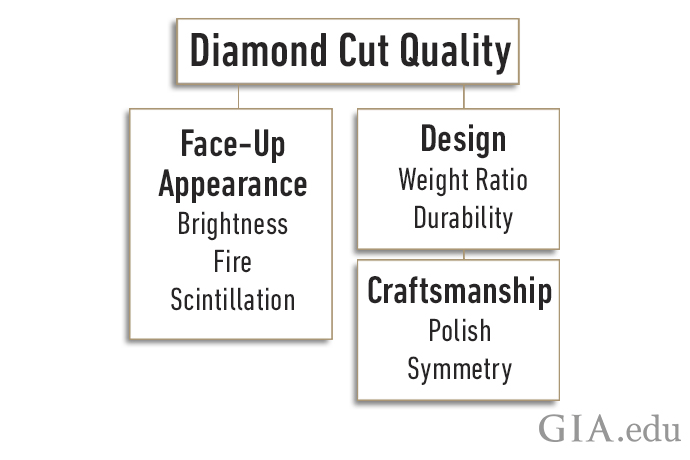
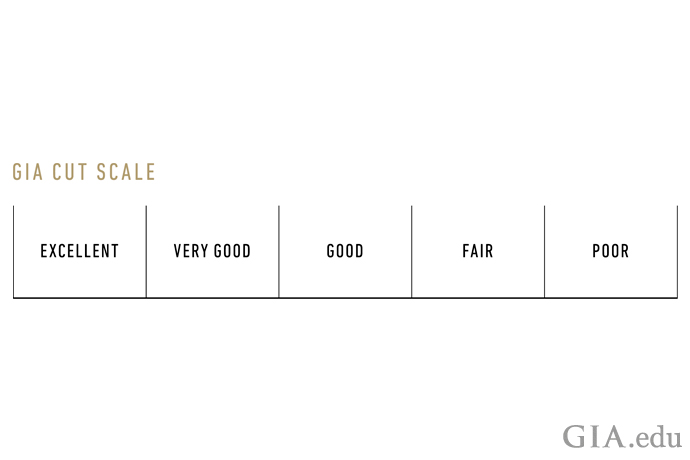
GIA Diamond Grading Reports: Understanding Diamond Cut Grades