GIA graded the 118.78 carat Graff Venus, claimed to be the largest D Flawless heart-shape diamond in the world. Courtesy: Graff Diamonds
Diamonds can be a significant financial and emotional investment. How do you know what you’re purchasing and what its quality or value is? A GIA Diamond Grading Report can help. It is not an appraisal; rather, it is a scientific blueprint of a diamond’s quality characteristics; it confirms that your diamond is natural and helps you compare diamonds when shopping.
In this article, we will cover:
What is a GIA Report?
GIA Diamond Grading Reports are issued for loose, natural diamonds in the D-to-Z color range that weigh 0.15 carats or more. GIA Diamond Grading Reports are not issued for diamond simulants, mounted diamonds or those that have undergone unstable treatments, such as fracture filling or coating. And while reports may be issued for diamonds that have been laser drilled or HPHT processed, reports will indicate that the diamond has been treated. Laboratory-grown diamonds are issued GIA Laboratory-Grown Diamond Reports that appear different from natural diamond reports in design but that also contain comprehensive 4Cs information.
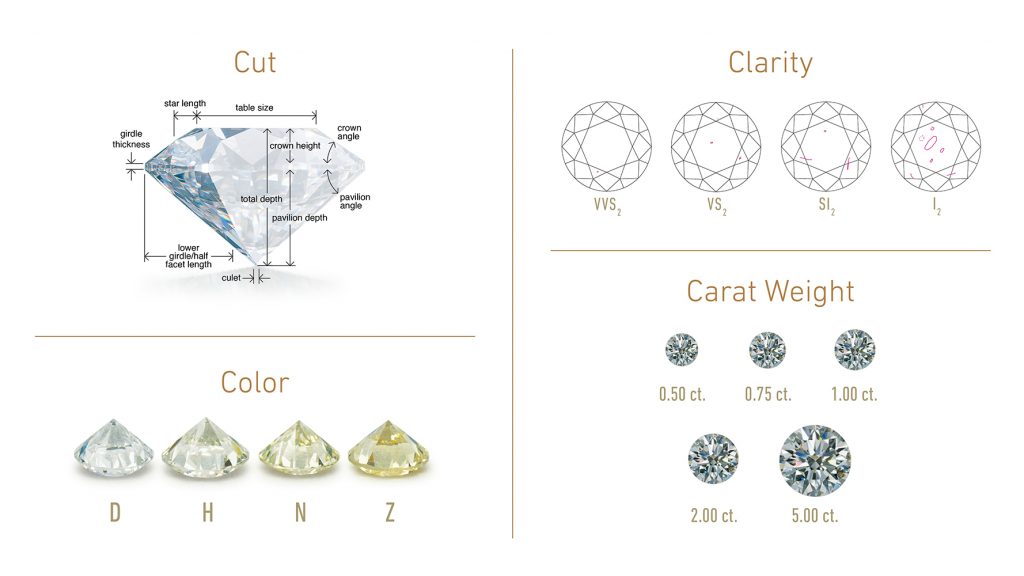
Each GIA Diamond Grading Report™ comes with a GIA Report Number that is unique to your diamond. You can look up your diamond’s information anytime on GIA Report Check by entering in this number. The report provides expert analysis of color, clarity, cut and carat weight, and also contains a proportions chart and plotting diagram that clearly shows a diamond’s inclusions and clarity characteristics, as well as offers additional information such as shape and cutting style, polish, symmetry and fluorescence. The GIA Diamond Origin Report also identifies the diamond’s country of origin, so that you can know your diamond’s impact on the communities that mined it. Learn about the different types of GIA diamond analysis services here.
Why do you need a GIA Report?
The GIA Diamond Grading Report is similar to house deeds or vehicle registrations in that it offers information on your purchase, and this information can be used to determine the value of your diamond. In addition to assuring you that you have a natural diamond, this report provides a 4Cs quality assessment (Color, Clarity, Cut and Carat Weight), with disclosure of any treatments used to enhance color or clarity. Knowing your diamond’s quality can help you compare prices and differences between diamonds to make a wise purchase.
Should you ever wish to sell your diamond, its value will be determined in part by its quality, which is communicated clearly on the report. In addition, the report contains many fascinating details about your diamond, including where its clarity characteristics or inclusions are located, whether it has fluorescence, and its specific angles and proportions. No two diamonds are exactly alike, even if they have the same 4Cs grades. The GIA Diamond Grading Report details the many characteristics that make your diamond unique!
Gem owners around the world seek out GIA reports because of their scrupulous and impartial evaluation. Diamond merchants recognize that stones bearing GIA reports have instant credibility in the marketplace. Those who buy, sell or curate the world’s most important diamonds, including the legendary Hope and the De Beers Centenary, rely on GIA.
*GIA is a nonprofit research and educational institute. It does not sell gems or jewelry, or represent people who sell them. Instead, GIA is an independent, impartial entity that researches, grades and sets standards for gems, and educates students and the public about gems.
Why did GIA create the 4Cs?
GIA created the 4Cs (Color, Clarity, Cut and Carat Weight) as a universal method for establishing the quality of any diamond, anywhere in the world. The 4Cs means two very important things—that diamond quality can be communicated in a universal language, and that diamond-buying consumers can know exactly what they are about to purchase.
Previously, jewelers used terms that were easily misinterpreted. For example, some diamonds were called “loupe clean” or “blue white” but there was no set standard behind these terms. Today, no matter where in the world you decide to buy your diamond, the jeweler will likely use terms such as VVS1 or D color.
The 4Cs of diamond quality give you a multitude of information about a diamond’s characteristics. You can rest assured in your diamond purchase when it comes with a GIA Diamond Grading Report.