Courtesy of JK & Co. Jewelers
A well-cut round brilliant-cut diamond should have a crisp, even face-up pattern of light and dark, and plenty of brilliance and fire.
A GIA cut grade for round brilliant-cut diamonds is one of the most important indicators of a diamond’s beauty and craftsmanship. Among the 4Cs—cut, color, clarity and carat weight—cut can be the most complex and the most important in bringing a diamond’s beauty to life. The way a diamond is cut determines how brilliantly it sparkles and how much fire it shows.
If you’re shopping for a round brilliant diamond engagement ring, understanding GIA’s cut grade system will help you choose a stone that truly shines. Here are six essential things to know before you buy.
1. Why Do GIA Cut Grades Matter?


Of the 4Cs of diamond quality, a diamond’s cut is said to have the greatest impact on a stone’s beauty. An expertly cut diamond will appear brilliant even if it has lower color and clarity grades, while a poorly cut diamond—even one with top color and clarity—will look dull.
Diamond cut grades also impact durability and value. For example, a diamond with a thin girdle may be at risk of chipping, while a diamond with a thick girdle may hide extra weight that makes the diamond cost more without increasing its visual impact.
GIA cut grades matter because they provide an objective, consistent way to measure how well a diamond interacts with light.
GIA’s comprehensive cut grade system evaluates seven key factors:
- Brightness
- Fire
- Scintillation
- Weight ratio
- Durability
- Polish
- Symmetry
These factors are combined to assign a grade ranging from Excellent to Poor. A higher cut grade means superior craftsmanship and optical performance—attributes that not only enhance a diamond’s beauty but also its market value.
For jewelers and buyers alike, it gives a universal language of quality, ensuring that every round brilliant diamond is judged by the same rigorous standard—so buyers can choose with both confidence and clarity.
2. Which Diamonds Get GIA Cut Grades?
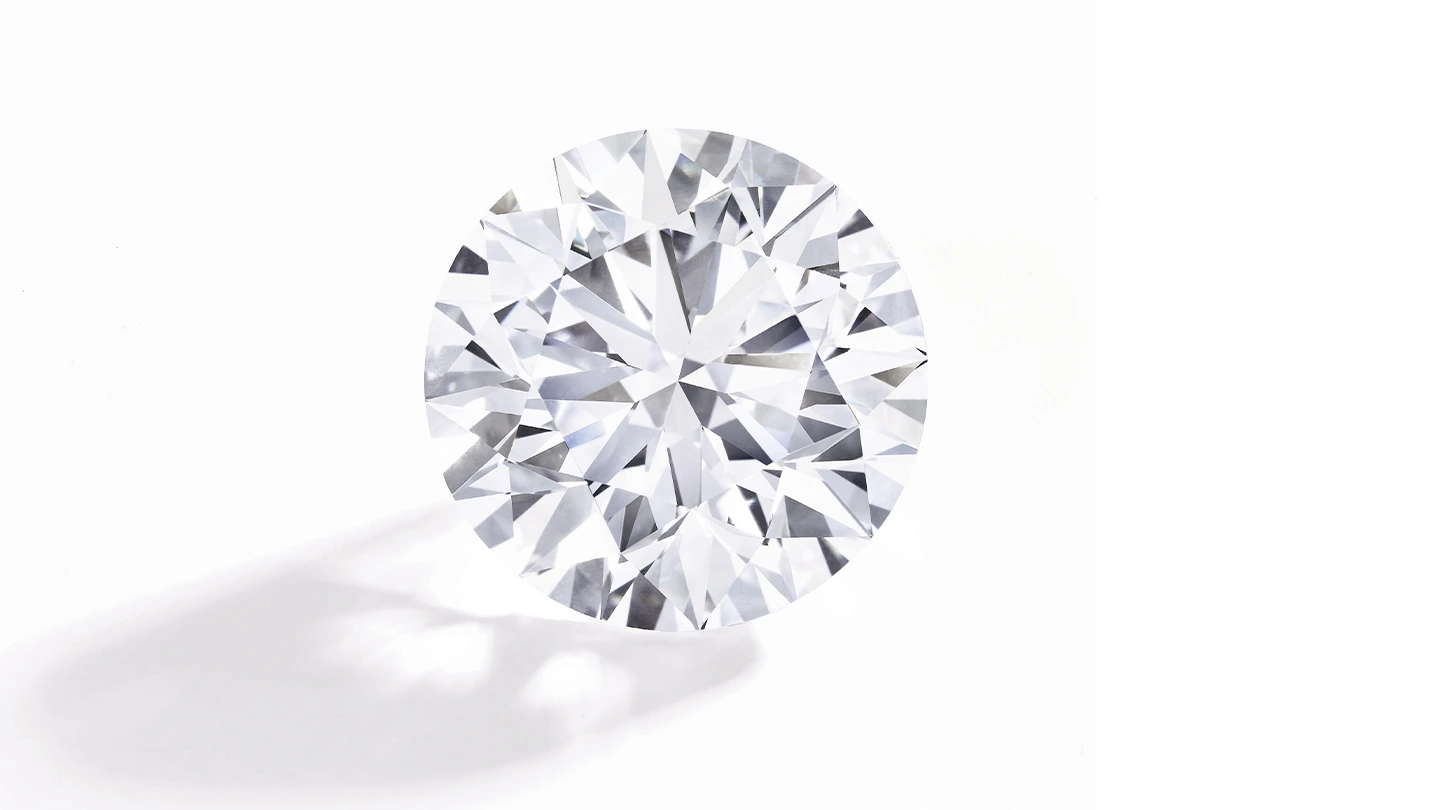

This 51.71-carat round brilliant diamond received top grades from GIA—D color, Flawless clarity and Excellent cut.

This 51.71-carat round brilliant diamond received top grades from GIA—D color, Flawless clarity and Excellent cut.
The round brilliant diamond is currently the only diamond shape that receives an official cut grade on GIA diamond reports. A diamond cut grade or diamond cut rating is unique to round brilliants because their facet pattern and light performance are standardized and well-defined. Through decades of research, GIA has established the precise relationships between angles, facet proportions and light return to consistently evaluate how well a round brilliant expresses its full beauty.
Other shapes, referred to as fancy cuts—including oval, pear, marquise, cushion, emerald and princess—do not currently receive an overall cut grade on GIA reports because their facet patterns and light behavior vary too widely for current standards to apply. However, different fancy shaped diamonds are meticulously evaluated for polish and symmetry, which reveal how precisely their facets are finished and aligned. Because cut quality plays such a vital role in how a diamond handles light, the better the cut grade, the more valuable the diamond.
In short, only round brilliant diamonds currently receive a formal cut grade, but every diamond is evaluated for polish and symmetry.
3. How Does GIA Determine Cut Grade?


GIA determines a diamond’s cut grade by evaluating how its proportions, symmetry and polish work together to influence light performance—the sparkle, fire and overall beauty we see.
This cut grading system took GIA 15 years to develop. Using advanced computer modeling, GIA analyzed tens of thousands of proportion combinations to understand how subtle differences in angles and facet sizes, and their relationships to each other, affect a diamond’s appearance. These findings were then tested through more than 70,000 human observations of real diamonds, helping GIA figure out which features people found the most attractive—and why.
The result is the GIA Cut Grading System, which evaluates round brilliant diamonds on a five-point scale: Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair or Poor.
When assigning a cut grade, GIA considers three key areas:
- Face-up appearance – how the diamond looks when viewed from above, including its brightness (white light return), fire (flashes of color) and scintillation (sparkle and light-dark pattern).
- Design – how well the diamond’s proportions balance beauty, durability and weight ratio. The girdle should not be too thick or thin. The pavilion should not be too shallow or deep, which can cause light leakage or reduce face-up size.
- Craftsmanship – the quality of the workmanship, including how precisely the facets are aligned and how well they are polished.
GIA evaluates the cut of a round brilliant diamond using seven key components—brightness, fire, scintillation, weight ratio, durability, polish and symmetry.
To assign an overall cut grade from Excellent to Poor, GIA uses the lowest rating the diamond receives for five of the seven components (brightness, fire, scintillation, weight ratio and durability). For example, if a diamond scores Poor in brightness, its overall cut grade cannot be higher than Poor.
Polish and symmetry are graded separately using GIA’s standard system. A diamond with Very Good polish and/or symmetry can still receive an Excellent cut grade if its light performance and proportions are exceptional.
A GIA cut grade offers a reliable, research-based measure of how well a round brilliant diamond interacts with light—helping you understand the true source of its beauty.
4. How Does Cut Impact Diamond Appearance?
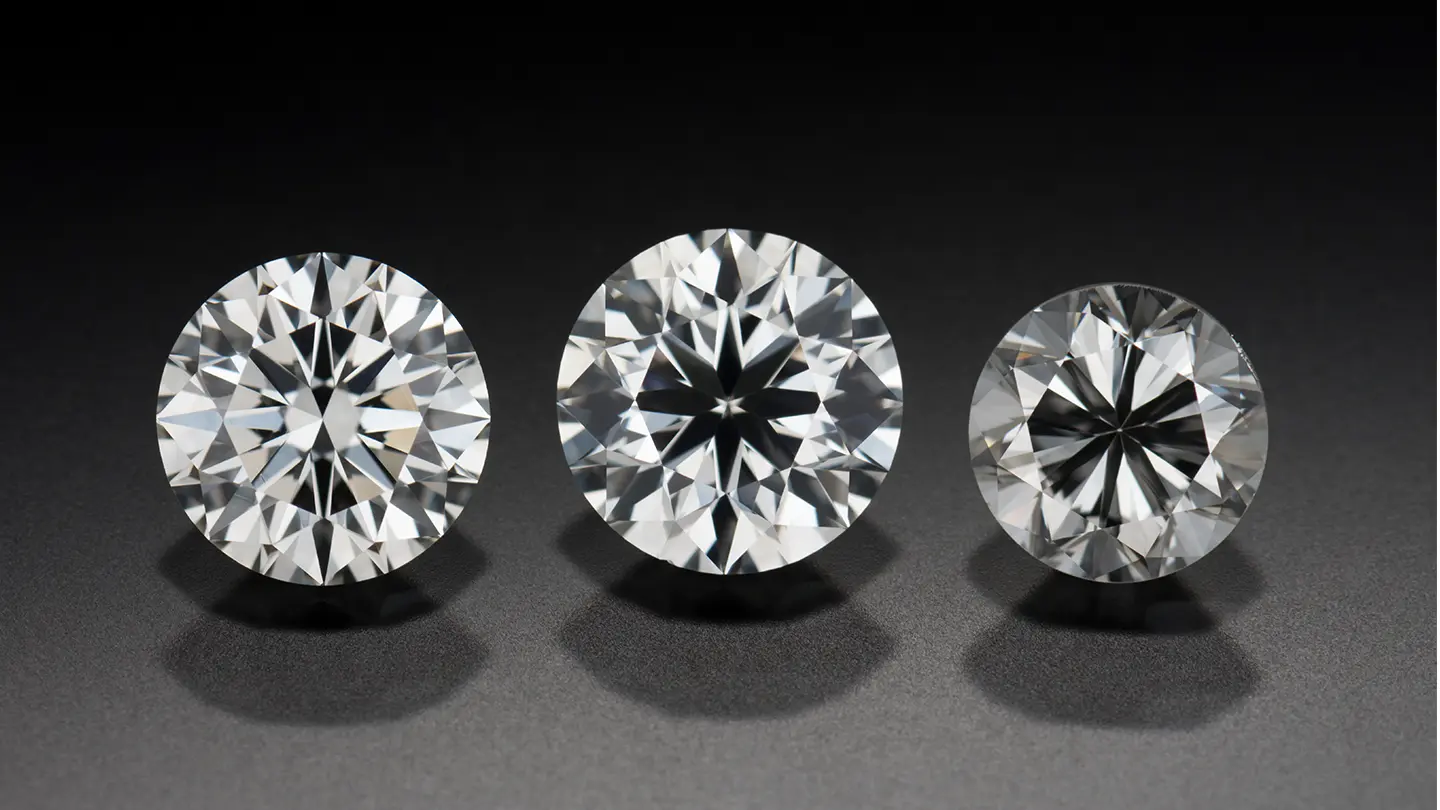
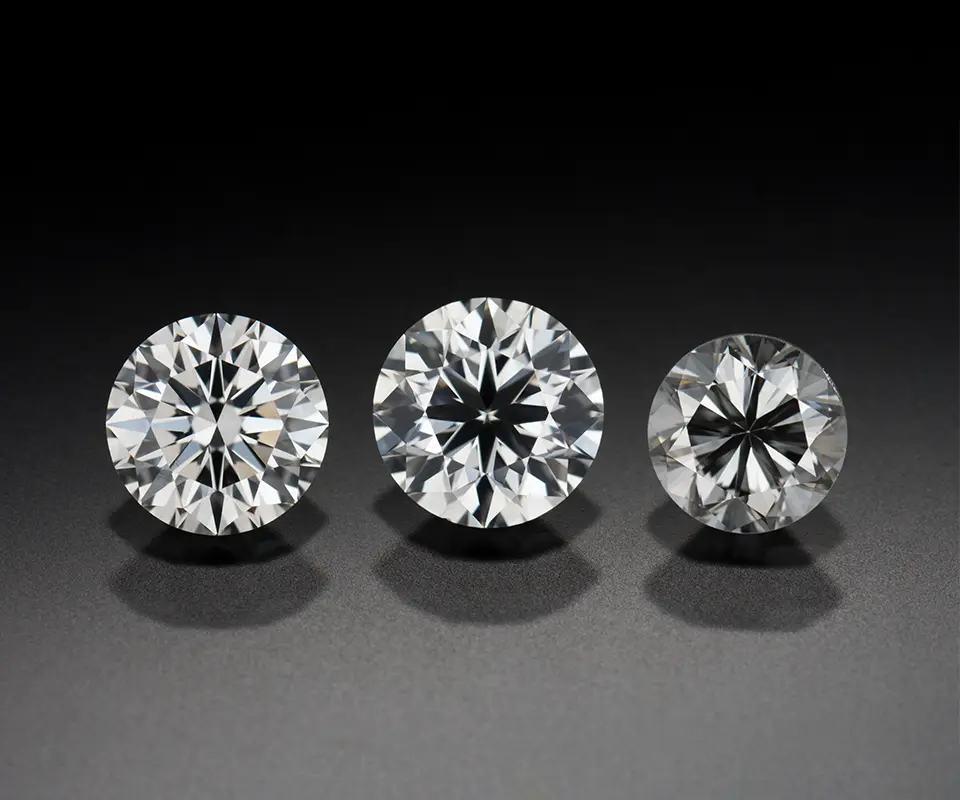


A diamond’s cut has significant influence on its overall beauty. Cut determines how light enters, reflects and exits the stone—creating the brightness, fire and scintillation that give a diamond its captivating sparkle.
A key part of GIA’s cut grade is the diamond’s face-up appearance, or how it looks when viewed from above, as it would appear in a ring. This view captures the play of light that makes diamonds so captivating.
- Brightness: The angles and proportions of an Excellent cut diamond return white light efficiently, creating a crisp contrast pattern that gives the diamond a bright, vivid appearance.
- Fire: When light disperses through a well-proportioned diamond, it breaks into flashes of spectral color—reds, blues, yellows—known as fire. An Excellent cut round brilliant diamond produces vivid color flashes while maintaining overall brightness.
- Scintillation: A well-cut diamond is symmetrical, with facets polished to a mirror-like finish that creates sharp contrast between light and dark areas. As the diamond or light source moves, the bright reflections off these facets appear to dance, giving the stone mesmerizing sparkle.
Cut is also shaped by two key finishing details:
- Symmetry: How neatly the diamond’s facets are aligned. Precise symmetry creates balanced patterns throughout the stone.
- Polish: The smoothness of each facet surface. Exceptional polish allows light to travel cleanly through the diamond, enhancing brilliance and overall light performance.
Together, these elements influence how efficiently a diamond interacts with light. The more precise the cut, the more brilliance, fire and sparkle the diamond will display.
5. How Does Proportion Impact Perceived Size?
A diamond’s proportions—the angles of its crown and pavilion and the size and placement of its facets—have a big effect on how large and sparkling it looks when viewed from above. Each facet acts like a tiny mirror, reflecting light back to your eye.
A well-proportioned diamond reflects more light across its surface, often appearing larger and brighter than one with poor proportions.
That’s why choosing a diamond with an Excellent or Very Good cut grade is often a wiser choice than opting for a larger diamond with a lower cut grade.
6. Which GIA Cut Grade Should You Buy?


Thanks to GIA’s research and standardized cut grading system, most round brilliant diamonds on the market today receive a grade of Excellent or Very Good. These grades indicate strong light performance and craftsmanship.
If you want maximum brilliance and fire, choose a diamond with an Excellent cut grade. Diamonds with Excellent cut grades should all appear bright, lively and well-proportioned—though their individual face-up patterns may differ, giving each one its own unique personality.
A Very Good cut diamond can also be a great choice, often offering beauty at a slightly lower price. Below Very Good, cut grades like Good, Fair or Poor typically show noticeable reductions in brightness or symmetry. These diamonds may appear darker, less fiery or smaller face-up.
In short, if your goal is a diamond that looks bright, balanced and full of life, aim for Excellent or Very Good cut grades—your best assurance of beauty and quality.
The Importance of Purchasing a Diamond with a GIA Report
When purchasing a diamond, a GIA Diamond Grading Report provides an expert evaluation of a round brilliant diamond’s cut grade, along with color, clarity and carat weight. It features precise measurements, a detailed proportions diagram and an unbiased assessment—giving you confidence in the diamond’s quality and a deeper appreciation for the craftsmanship behind it.
A GIA report also brings transparency to the buying process by clearly stating whether a stone is natural or laboratory-grown and noting any treatments. For consumers, it offers peace of mind. For retailers, it builds trust.
By understanding cut grade and relying on GIA’s independent diamond grading, you can make informed decisions and fully appreciate the craftsmanship, science and beauty behind every diamond.
